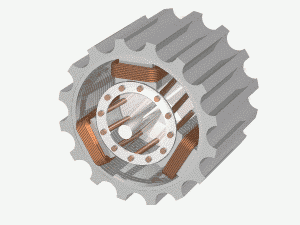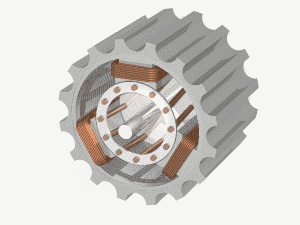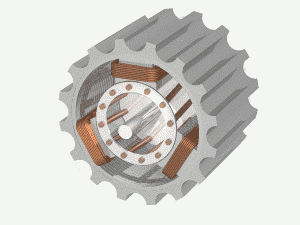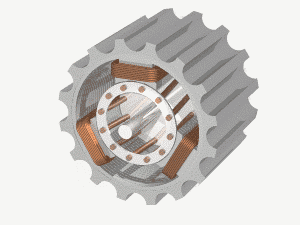
Q1: What causes a motor to turn?
A1: There are two parts to
Q2. Why would you use a phase splitter and a three-phase motor instead of a single-phase motor?
A2: It is possible that at the moment single-phase power is all that is available, but in the future three-phase power is expected. Therefore, if you purchase the three-phase motor and a phase splitter, the wiring will be in place, the motor will be at the desired location, and the expenses will be cut down. There is also less maintenance on three-phase motors; this one fact will often influence the use of a phase splitter.
Q3. How is regulation obtained in a motor?
A3: The motor at start emf
Q4. Does an ac
A4: No. It must slip below synchronous speed so that an effective voltage will be produced.Q5. What is a synchronous motor?
A5: A synchronous motor is almost exactly the same as an alternator. The field must be excited by direct current. The motor runs at the same speed or at a fixed multiple of the speed of the alternator supplying the current for its operation. Should it slip, the motor will pull out and stop since it must run pole for with pole the alternator.
A6: It is a synchronous motor running without mechanical load on the line, with its field overexcited for power-factor correction.
Q7. If the field on a
A7: The motor would try to run away with itself, or, in other words, the motor would reach a very high speed and might destroy itself.
dc on ac dc dc
Q10. How can the direction of rotation of a
A10: By reversing either the field leads or the armature leads, but not both.